
A herniated disc is a common disease of the spine that can cause severe pain and disability.
Here we would like to offer you a comprehensive insight into the anatomy, development, symptoms and treatment options of a herniated disc.
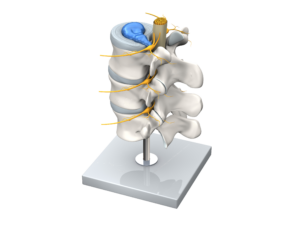 The spine consists of a series of vertebrae that are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. These discs consist of a solid outer ring, the annulus fibrosus, which surrounds the nucleus pulposus, a soft, gel-like core. A herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus leaks through cracks or weak points in the annulus fibrosus and presses on the surrounding nerve structures. These changes are very often diagnosed as incidental findings in MRI scans and do not always cause symptoms. It is therefore essential to correlate the clinical symptoms with the MRI images.
The spine consists of a series of vertebrae that are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. These discs consist of a solid outer ring, the annulus fibrosus, which surrounds the nucleus pulposus, a soft, gel-like core. A herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus leaks through cracks or weak points in the annulus fibrosus and presses on the surrounding nerve structures. These changes are very often diagnosed as incidental findings in MRI scans and do not always cause symptoms. It is therefore essential to correlate the clinical symptoms with the MRI images.
The development of a herniated disc can be influenced by various factors. Over time, the intervertebral disc can degenerate and lose elasticity, which can lead to tears in the annulus fibrosus. Sudden movements, heavy physical strain or injuries such as an accident can also lead to a herniated disc. In addition, genetic predispositions or certain lifestyle factors can increase the risk.
A herniated disc can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and neurological deficits. The most common symptoms include
1. back pain: a herniated disc can cause acute or chronic back pain, which can manifest itself differently depending on the location of the herniation and individual factors. The pain can worsen when certain movements are performed, such as bending, lifting or twisting.
2. radiating pain: The pain of a herniated disc often radiates to neighbouring areas of the body, such as the legs or arms. This may be due to pressure on the nerve roots, which are irritated by the herniated part of the disc.
3. paraesthesia and tingling: The pressure on the nerve roots can also lead to numbness, tingling or “formication” in the affected areas of the body. These sensory disturbances can range from the back or neck regions to the extremities.
4. loss of strength: A herniated disc can affect the normal function of the muscles supplied by the affected nerves. This can lead to muscle weakness or a feeling of “weakness” in the arms or legs, which can impair mobility.
5. impairment of reflexes: In some cases, a herniated disc can lead to impaired reflexes controlled by the affected nerve roots. This can be caused by the pressure on these nerves and should be clarified as soon as possible.
At ECOM® we have a wide range of different therapeutic approaches and options at our disposal, which can be used depending on the symptoms.
In collaboration with our physiotherapy and training therapist colleagues, we design an individual treatment plan for you and accompany you on your way to freedom from pain. Of course, this is preceded by a detailed examination and, if necessary, the use of imaging procedures (X-ray, MRI) to confirm the diagnosis.
Find out all about our treatment methods here:
Do you have questions about treatment and therapy for a slipped disc? Our spine specialist will be happy to advise you in detail in a personal consultation. Simply make an appointment. We look forward to seeing you.

Specialist in orthopaedics and trauma surgery, manual medicine/chiropractic therapy
Sehr geehrte Besucher,
Sie verlassen nun den Internetauftritt der ECOM® – Praxis für Orthopädie, Sportmedizin und Unfallchirurgie Dr. Erich Rembeck, Dr. Alexander Rauch, Prof. Dr. Hans Gollwitzer, Prof. Dr. Patrick Weber – Ärztepartnerschaft aus München.
Sie werden weitergeleitet auf den Internetauftritt von ECOM – Zentrum für Regenerative Medizin und Stammzelltherapie Dr. Erich Rembeck, Dr. Alexander Rauch, Prof. Dr. Hans Gollwitzer, Prof. Dr. Patrick Weber in Thiersee, Österreich.
Die im folgenden beschriebenen Therapien finden ausschließlich in Österreich statt und sind von der Ärztekammer Tirol, sowie der Österreichische Agentur für Gesundheit und Ernährungssicherheit (AGES) genehmigt.
Bitte bestätigen Sie mit OK. Wir bedanken uns für Ihr Interesse!